NFT vs DWC Hydroponics: 2025 Profitability Guide for Commercial Growers
For commercial growers in the US and Canada aiming for peak profitability in 2025, selecting the right hydroponic system is paramount. Hydroponics bypasses soil limitations, boosting efficiency and yield using nutrient-rich water. As demand for local produce rises, understanding the NFT vs DWC hydroponics debate is crucial.
This guide directly compares two leading methods: Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and Deep Water Culture (DWC). Both outperform soil, but their unique characteristics impact your bottom line. We’ll dissect the critical factors for North American growers – initial investment, operational costs, yield potential, and risks – providing a clear hydroponic farming cost and profit analysis to inform your decision in the NFT vs DWC landscape.

Understanding Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Hydroponics for Commercial Scale
What is Nutrient Film Technique? (nutrient film technique definition)
So, what exactly is Nutrient Film Technique? Imagine plants growing with their roots suspended, usually in slightly sloped channels. A very thin, continuous “film” of nutrient solution flows along the bottom of the channel, bathing the lower roots. The upper roots remain exposed to the air, getting plenty of oxygen. This continuous flow and air access are hallmarks of nft hydroponics.
How NFT Hydroponics Works Commercially
 In a commercial NFT system, water is pumped from a reservoir to the high end of the channels and flows back down via gravity, returning to the reservoir to be recirculated. It’s known for being highly efficient with water and nutrients, which can lower operating costs. Plus, the open channels make it easy to check root health. NFT works best for lightweight, fast-growing crops like leafy greens (lettuce, spinach), herbs (basil, mint), and strawberries.
In a commercial NFT system, water is pumped from a reservoir to the high end of the channels and flows back down via gravity, returning to the reservoir to be recirculated. It’s known for being highly efficient with water and nutrients, which can lower operating costs. Plus, the open channels make it easy to check root health. NFT works best for lightweight, fast-growing crops like leafy greens (lettuce, spinach), herbs (basil, mint), and strawberries.
However, NFT systems have critical vulnerabilities. Because there’s only a thin film of water, a pump failure or power outage can quickly dry out roots, potentially leading to total crop loss within hours – reliable pumps and backup power are essential. The shallow water is also sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and vigorous root growth can clog the narrow channels. While nutrient film technique hydroponics is efficient, it demands careful management.
Commercial Advantages & Disadvantages of Nutrient Film Technique
Advantages:
- Water/Nutrient Efficiency: Highly conservative, lower operational costs.
- Root Oxygenation: Promotes healthy roots.
- Space Efficiency: Ideal for vertical setups.
- Reduced Soil Issues: Eliminates soil pests/diseases.
- Easy Inspection: Exposed roots simplify monitoring.
Disadvantages & Risks:
- Pump Failure Susceptibility: Critical Risk – rapid root drying, potential total loss. Backup power essential.
- Clogging Risk: Roots can block channels/drains.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Low water volume reacts quickly to air temp changes.
- Rapid Disease Spread: Shared film facilitates pathogen movement.
- Low Buffering: Small volume means rapid pH/EC shifts.
- Plant Size Limits: Best for lightweight crops.
Best Crops for Commercial NFT: Leafy Greens (Lettuce, spinach), Herbs (Basil, mint), Strawberries.
Understanding Deep Water Culture (DWC) Hydroponic Systems for Commercial Scale
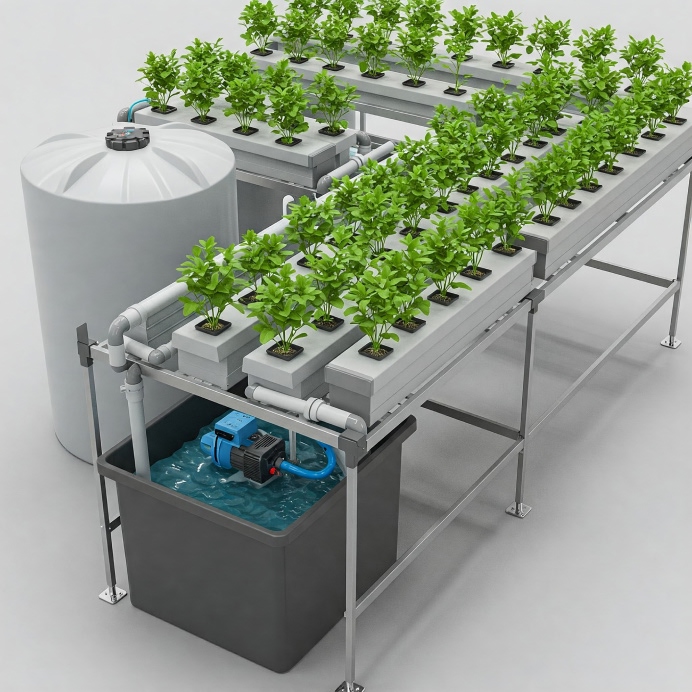
Now let’s look at Deep Water Culture, often called dwc hydroponic. In this method, plants sit in net pots on rafts (like Styrofoam) or lids that float on or cover a deep reservoir of nutrient solution. The plant roots are continuously submerged in this large body of water.
Because the roots are fully underwater in a dwc hydroponic system, providing enough oxygen is absolutely critical. This is done using air pumps and air stones that constantly bubble oxygen into the water, preventing root suffocation. The large volume of water provides excellent access to nutrients and acts as a buffer, making the root zone temperature much more stable than in NFT.

How DWC Hydroponics Works Commercially
In a dwc hydroponic system, roots are submerged 24/7, requiring constant oxygenation:
- A large Reservoir/Tank/Pond holds the nutrient solution.
- Rafts or Lids hold plants in Net Pots above/on the water.
- An Aeration System (air pumps, stones) bubbles oxygen into the water. This is vital.
- Recirculating DWC (RDWC) connects multiple tanks for larger scales.
Commercial Advantages & Disadvantages of DWC Hydroponic Systems
What are the advantages of DWC hydroponics?
A major advantage of DWC is its resilience. If the air pump fails, the roots remain submerged, giving you hours or even days to fix the issue before oxygen depletion becomes critical – a significant safety net compared to NFT. DWC can also support larger, heavier plants like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers (though they might still need external support), offering more crop flexibility.

What are the cons of deep water culture?:
The downsides? Managing water temperature in such a large volume can be energy-intensive, potentially requiring costly chillers or heaters. Keeping nutrient levels, pH, and dissolved oxygen consistent throughout a large static tank can be challenging (Recirculating DWC, or RDWC, helps but adds complexity). Initial water use is higher, and cleaning large tanks is a significant task. Poorly oxygenated or managed water can also become a breeding ground for root diseases.
Best Crops for Commercial DWC: Leafy Greens/Herbs (Lettuce, basil), Larger Fruiting Plants (Tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers – with support), Strawberries.
Comparing Costs, Risks, and Operations: NFT vs DWC
Choosing between NFT vs DWC hydroponics requires weighing their commercial differences for US/Canadian growers. The hydroponics dwc vs nft decision impacts everything from setup cost to daily operations.

Initial Investment Costs (US/Canada Focus)
- System Hardware: NFT’s channels vs. DWC’s tanks/aeration. Basic DWC might be cheaper ($1.90-$2.75/sq ft less), but large/RDWC can equalize costs. Comparing nft vs dwc hydroponics costs requires specific quotes.
- Infrastructure: Greenhouse, climate control, lighting, etc., are major costs for both ($2.50-$5.00/sq ft/year).
- Total Farm Cost: Highly variable ($100k – $1M+ USD range for vertical farms).
Table 1: Estimated Commercial Hydroponic Setup Costs (NFT & DWC) – US/Canada Indicative Ranges
Operational Costs
- Water & Nutrients: NFT generally more efficient. DWC uses larger volumes.
- Energy: NFT pumps vs. DWC aeration. DWC may need more for temp control; NFT more sensitive to ambient temp.
- Labor: NFT needs pump/clog checks; DWC needs aeration/volume checks. Automation significantly cuts labor for both.
System Scalability & Management
- Scalability: Both are scalable (NFT modular/vertical, DWC via RDWC).
- Management Complexity: NFT requires precision (low buffer). DWC needs stability management (large volume). DWC often considered more forgiving manually in the dwc vs nft hydroponics comparison.
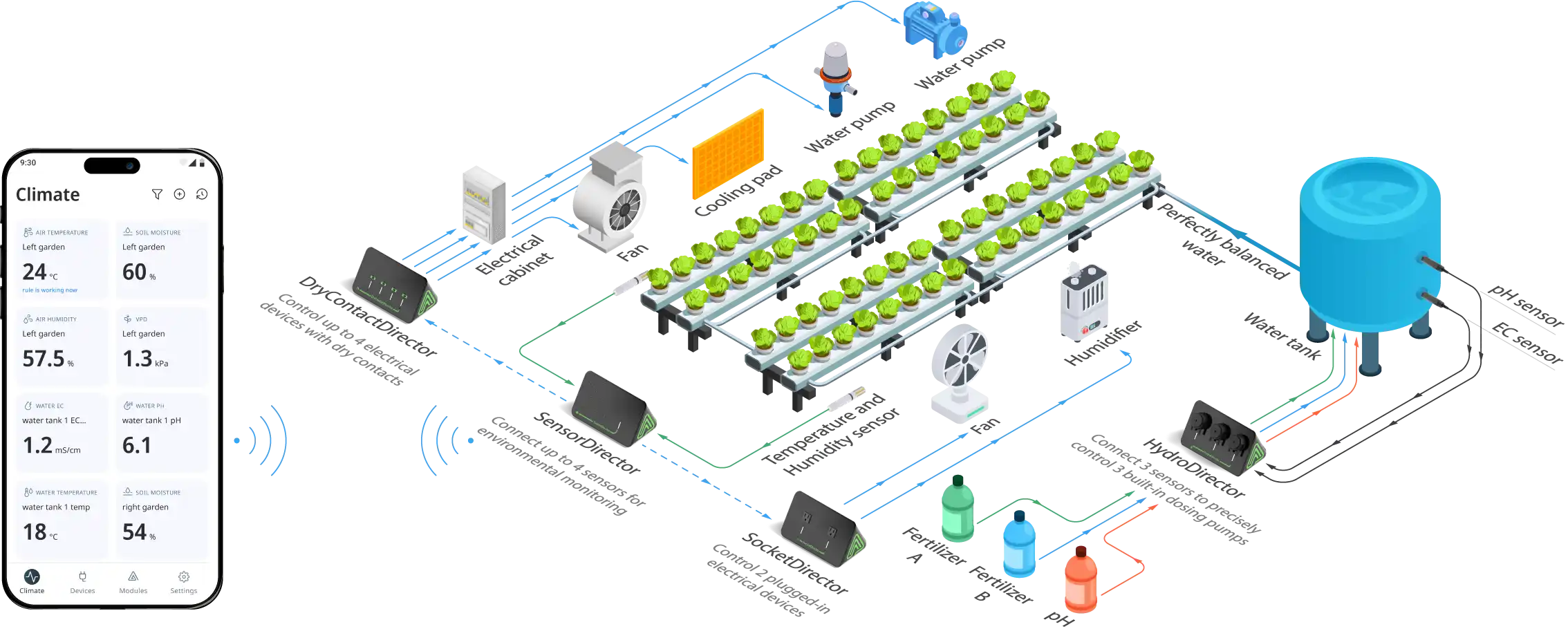
The GrowDirector System scales easily, no matter what type of growing method or crop you use – READ MORE
Risk Factors
- System Failure: NFT highly vulnerable to pump failure. DWC more resilient to aeration failure. The hydroponics nft vs dwc risk profile differs significantly here.
- Disease: Both susceptible; rapid spread in NFT film vs. risk in poorly managed DWC.
- Environmental Sensitivity: NFT roots sensitive to air temp; DWC water temp stable but needs energy to control.
Table 2: NFT vs. DWC Head-to-Head Commercial Comparison Summary (US/Canada Focus)
Yield Potential and Crop Suitability in the NFT vs DWC Debate
While hydroponics dramatically increases yield over soil farming, the difference between well-managed NFT and DWC systems growing the same crop (like lettuce) is often minimal. Your management practices likely have a bigger impact than the system type itself.

Does DWC Increase Yield? Not necessarily more than NFT for shared crops. However, DWC’s ability to support larger, potentially higher-value crops (tomatoes, cucumbers) can lead to higher revenue potential per square foot.
Crop Flexibility
The key difference lies in crop flexibility. NFT excels with lightweight greens, herbs, and strawberries but isn’t suited for heavier plants without extra support. DWC handles leafy greens and herbs effectively and can support larger, potentially higher-margin crops like tomatoes and cucumbers. So, while DWC doesn’t guarantee higher yield per se, its flexibility might lead to higher revenue if your market demands those larger crops. This crop suitability is a major factor in the hydroponics nft vs dwc decision.
Crop Cycle Times and Suitability
Hydroponics generally accelerates growth. Cycle times for shared crops are similar between NFT and DWC.
- NFT: Excels with lightweight plants (leafy greens, herbs, strawberries). Limited flexibility. This defines its niche in the nft vs dwc hydroponics comparison.
- DWC: Effective for leafy greens/herbs, and better supports larger plants (tomatoes, peppers). Greater crop flexibility.
Profitability Analysis: NFT vs DWC – Which Offers Better ROI?
The core question: which system offers better ROI in the NFT vs DWC showdown? A thorough hydroponic farming cost and profit analysis is needed. When analyzing profitability (ROI), consider the trade-offs. NFT offers potential operational savings (water, nutrients) but carries higher immediate risk and limits crop options. DWC provides stability and flexibility but might have higher operational costs (water volume, temp control) and requires diligent aeration management.
High startup costs demand focus on ROI. Both systems can be profitable, but success depends on management, market, and aligning the system choice (NFT or DWC) with the business model.
Cost vs. Revenue Drivers:
- Costs: High CapEx, ongoing OpEx (energy, water, nutrients, labor).
- Revenues: Yield, cycles/year, market price, crop choice.
NFT vs. DWC Hydroponics Profitability Comparison
Table 3: Profitability Factor Summary (NFT vs. DWC)
The Role of Automation in the NFT vs DWC Decision (GrowDirector Insights)
Modern automation systems, like GrowDirector, significantly impact the NFT vs DWC hydroponics comparison. By automatically monitoring and adjusting crucial parameters (like pH, EC, water temperature, oxygen levels, pumps, lighting), these systems drastically reduce labor costs (we’ve seen 46-60% savings), improve plant health consistency, and crucially, mitigate risks.
For NFT, automation handles the precise monitoring required and provides alerts for pump issues. For DWC, it ensures stable water quality and oxygen levels, addressing key management challenges. Automation makes both systems easier and safer to run, shifting the decision away from just management difficulty towards the fundamental differences: NFT’s resource efficiency vs. DWC’s stability and crop flexibility. Factoring in robust automation should be part of any serious NFT vs DWC evaluation. Read real Case Studies – CLICK HERE.
Quick Answers: NFT vs DWC Fundamentals
Here are brief answers to common questions comparing hydroponics NFT vs DWC:
- NFT Basics? Shallow nutrient film flows past bare roots in channels.
- DWC Basics? Roots submerged in a deep, oxygenated nutrient reservoir.
- Key Difference? NFT = thin film, roots partly in air, high pump failure risk. DWC = deep water, roots submerged, needs aeration, more stable temp/resilient to power loss.
- DWC Advantages? Temperature stability, resilience to power outages (vs. NFT pump failure), suits larger plants.
- DWC Cons? Needs constant aeration, water temp control can be costly, managing large water volumes.
- Does DWC Yield More? Not necessarily for the same crop vs. NFT. Offers higher revenue potential through broader crop options.
Which System is Right for Your Greenhouse?
Choosing between Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and a DWC hydroponic system is a strategic decision with no single “best” answer. The most profitable path for your commercial greenhouse in the NFT vs DWC hydroponics landscape depends on your specific situation:
- Choose NFT if: Your focus is highly efficient production of leafy greens, herbs, or strawberries; water/nutrient costs are primary concerns; you plan vertical integration; and you have the budget for automation or expertise to manage its sensitivity.
- Choose DWC if: Crop flexibility to meet market demands is key; system stability and resilience against power failures are critical; you can manage potentially higher water/energy costs; or you prefer a system often seen as more forgiving (especially with automation).
Remember, investing in automation like GrowDirector can significantly boost the efficiency and reduce the risks of bothsystems. Thorough planning that aligns your chosen system (NFT or DWC) with your market, budget, operational capabilities, and risk tolerance is the foundation for success.
Ready to explore how automation can optimize your chosen system? Contact the GrowDirector team today for a consultation tailored to North American growers!